
Power over Ethernet (PoE) power efficiency can be calculated by comparing the input power at the power source (e.g., PoE injector or switch) with the output power received by the powered device (PD), such as an IP camera, VoIP phone, or wireless access point.Here's the general process for calculating PoE power efficiency:
1. Measure Input Power (P_in)
Input Power (P_in): This is the power consumed by the PoE switch or PoE injector. It's typically measured in watts (W) and includes the losses in the cabling and any power dissipated in the switch or injector components.
2. Measure Output Power (P_out)
Output Power (P_out): This is the actual power delivered to the powered device (PD). It's also measured in watts and is the useful power received by the device for its operation.
3. Efficiency Formula
The PoE power efficiency can be calculated using the following formula:
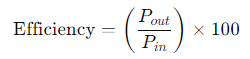
Where:
???? = Power received by the powered device (W)
??? = Power consumed by the PoE source (W)
4. Example Calculation
Input Power (P_in): 30W (measured at the PoE injector or switch)
Output Power (P_out): 25W (measured at the powered device)
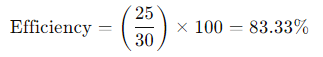
In this example, the PoE system operates at an efficiency of 83.33%.
Considerations:
Cable Length and Quality: The longer the cable and the lower its quality, the more power loss due to resistance, reducing efficiency.
PoE Standards: Different PoE standards (PoE, PoE+, PoE++) have different power levels and efficiencies. PoE++ delivers more power but may have more loss over the cable.
Switch Design: High-quality PoE switches with better power management features tend to offer higher efficiency.
By optimizing your PoE system—using quality cabling, efficient switches, and proper power management—you can maximize power efficiency.