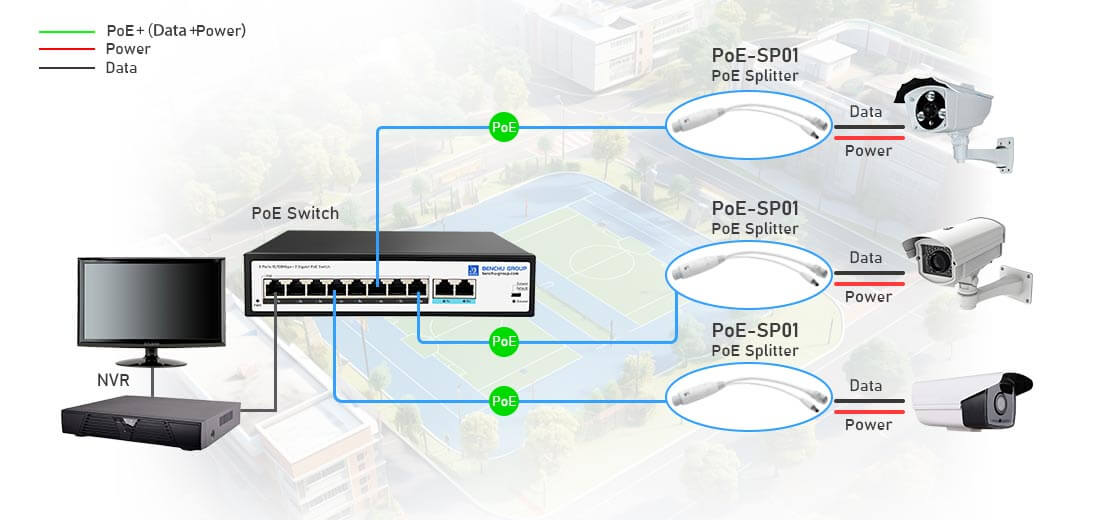
A Power over Ethernet (PoE) splitter is a device that allows you to separate the power and data signals that are combined in a PoE cable. This enables you to use a non-PoE (Power over Ethernet) powered device with an Ethernet cable that is delivering power. Essentially, a PoE splitter makes it possible to power a device that is not inherently designed to receive power through Ethernet.
How it Works:
1. PoE Delivery:
In a typical PoE setup, both power and data are transmitted over the same Ethernet cable, which allows devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, or wireless access points to receive power and data using just one cable.
The power is supplied by a PoE injector or PoE switch. There are two main standards for PoE: IEEE 802.3af (PoE) and IEEE 802.3at (PoE+), with the latter providing more power.
2. Splitting the Signals:
A PoE splitter takes the incoming Ethernet cable with both power and data and separates them into two different outputs:
Data Output: For Ethernet communication (usually on standard 10/100/1000 Mbps speeds).
Power Output: A separate output that provides power, typically in the form of a DC voltage (e.g., 5V, 9V, 12V, 24V), depending on the device's requirements.
3. Connection to Non-PoE Devices:
The PoE splitter then allows the device that requires separate power (e.g., an older IP camera, a networked device without PoE capability) to operate by supplying the correct voltage and amperage, as per the device’s power needs.
The data continues through the Ethernet cable, while the power is delivered through a separate cable or connector (e.g., DC jack).
Key Features:
--- Voltage Output Flexibility: PoE splitters come in various models that provide different output voltages (e.g., 5V, 9V, 12V). It is important to select the appropriate model based on the voltage requirements of the device you are powering.
--- Plug-and-Play Operation: Most PoE splitters are designed for easy, plug-and-play use. You simply connect the Ethernet cable from the PoE switch or injector to the splitter, and then connect the split outputs to the device requiring data and power.
--- Compact and Cost-Effective: PoE splitters are small, inexpensive devices that are often used to enable legacy devices to be part of a PoE-powered network without the need for an entirely new infrastructure.
Benefits of Using a PoE Splitter:
--- Flexibility in Device Integration: It makes it possible to integrate non-PoE devices into a PoE network, reducing the need for additional power cables or outlets.
--- Simplified Installation: With a PoE splitter, you can use a single Ethernet cable for both power and data, making installations cleaner and more straightforward.
--- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: You don’t need to upgrade devices to PoE-enabled versions, as the splitter can provide the necessary power for non-PoE devices.
Example Use Case:
Let’s say you have a network switch that supplies PoE power, but you have an old IP camera that is not PoE-compatible. By adding a PoE splitter, you can easily power the camera using the existing PoE cable while still ensuring it has access to the network via the Ethernet connection.
Limitations:
--- Power Limitations: The power provided by a PoE splitter is limited by the amount of power the PoE source can supply. If the source is providing low wattage (e.g., 15.4W or 25.5W), it might not be sufficient to power high-demand devices.
--- Compatibility Issues: You must ensure that the voltage output from the PoE splitter matches the requirements of the device being powered. Over-voltage or under-voltage can damage the device.
Conclusion:
A PoE splitter is a simple and effective solution to enable devices that do not support PoE to receive power from a PoE network. It is ideal for applications where you need to keep the network infrastructure consistent but need to power older or non-PoE devices.