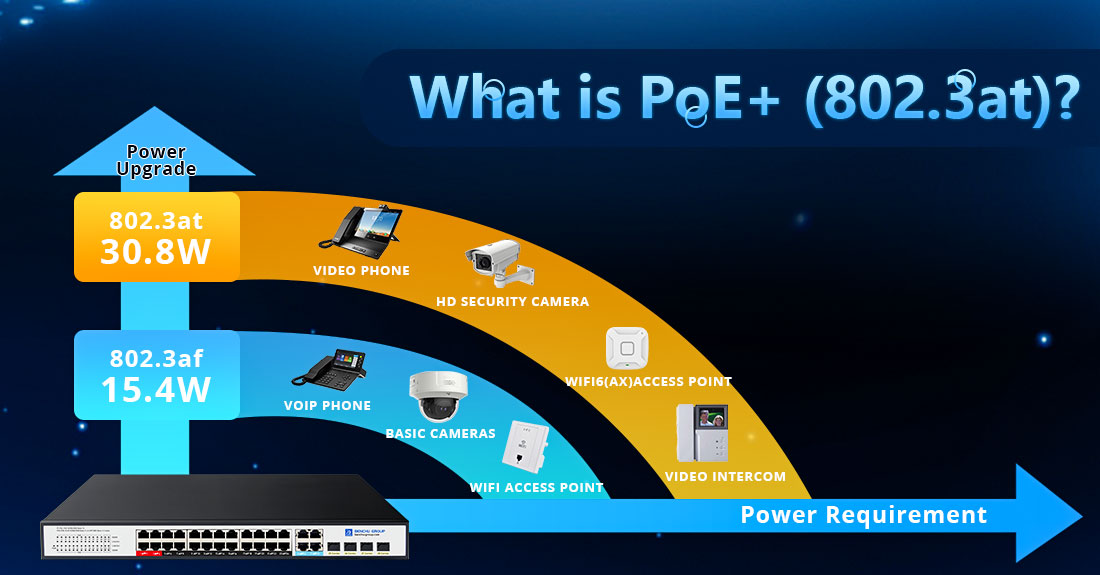
PoE+ (802.3at) is an enhanced version of Power over Ethernet (PoE), standardized under the IEEE 802.3at specification. It builds upon the original PoE standard (802.3af) by providing more power to connected devices, making it suitable for powering more demanding network equipment. Here’s a detailed breakdown of PoE+:
Key Features of PoE+ (802.3at):
1.Increased Power Output:
--- PoE (802.3af) delivers a maximum of 15.4 watts of power per port to connected devices.
--- PoE+ (802.3at) significantly increases the available power to 30 watts per port. After accounting for power losses in the cable, the actual available power at the device (powered device or PD) is about 25.5 watts.
--- This higher power output enables PoE+ to support devices with greater power requirements.
2.Device Support:
PoE+ (802.3at) is designed to power more demanding network devices that cannot be powered efficiently by standard PoE. Some examples include:
--- PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) cameras with advanced features like motorized controls and heaters.
--- Wireless access points (APs) with multiple radios, MIMO technology, or higher data transmission requirements.
--- VoIP phones with video screens or additional features.
--- Video conferencing equipment.
--- Some network switches or IP cameras with added features like night vision or additional sensors.
3.Backward Compatibility:
--- PoE+ (802.3at) is fully backward compatible with PoE (802.3af) devices, meaning that a PoE+ switch can power both PoE and PoE+ devices.
--- However, PoE devices that comply only with the 802.3af standard will still receive a maximum of 15.4 watts, even when connected to a PoE+ switch.
4.Cable Requirements:
--- PoE+ (802.3at) works over standard Cat5e or higher Ethernet cables, just like regular PoE. However, to achieve optimal performance and minimize power losses, it is recommended to use Cat5e, Cat6, or better cabling, especially for longer cable runs.
--- PoE+ uses two pairs of wires (just like PoE) to deliver both power and data.
Power Negotiation (LLDP):
--- PoE+ uses a more advanced power negotiation system known as Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) to negotiate the exact amount of power a device needs. This makes PoE+ more energy-efficient as it can supply just the right amount of power rather than delivering a fixed wattage.
Differences Between PoE (802.3af) and PoE+ (802.3at):
| Feature | PoE (802.3af) | PoE+ (802.3at) |
| Power Output | Up to 15.4 watts per port | Up to 30 watts per port |
| Available Power at Device | Up to 12.95 watts (after losses) | Up to 25.5 watts (after losses) |
| Device Types | VoIP phones, basic IP cameras, small APs | High-end cameras, multi-radio APs, PTZ cameras |
| Backward Compatibility | Compatible with PoE devices (802.3af) | Backward compatible with PoE (802.3af) |
| Cable Type | Cat5 or higher | Cat5e or higher recommended |
Applications of PoE+ (802.3at):
PoE+ is ideal for devices that require more power than what standard PoE can provide, such as:
--- Surveillance systems: Advanced IP cameras, especially those with features like motorized zoom or heating elements.
--- Wireless networks: High-performance wireless access points (APs) in businesses or public spaces.
--- VoIP phones: Phones with large color screens or video conferencing capabilities.
--- Digital signage: Larger or more complex displays that need higher power.
Summary:
PoE+ (802.3at) offers a higher power output than the original PoE standard, making it suitable for more power-hungry devices while maintaining backward compatibility with older PoE standards. This makes it a flexible and scalable solution for modern network infrastructure, especially in settings like security, Wi-Fi networks, and smart buildings.