
The packet forwarding rate of an industrial switch refers to the speed at which the switch can process and forward data packets through its network ports. It is measured in packets per second (pps) and determines the switch's ability to handle network traffic effectively. The packet forwarding rate is crucial for evaluating a switch’s performance, especially in high-demand industrial environments where real-time data exchange is essential.
Key Factors Influencing Packet Forwarding Rate:
1.Switching Capacity: The total throughput a switch can handle across all its ports, often expressed in Gbps.
2.Port Speed: Higher-speed ports (e.g., 1G, 10G, 40G, or 100G) can forward more packets per second than lower-speed ports.
3.Layer 2 vs. Layer 3 Switching: Layer 2 switches typically have higher packet forwarding rates since they deal with MAC address-based forwarding, while Layer 3 switches must handle more complex IP-based routing.
1. Understanding Packet Forwarding Rate
The packet forwarding rate indicates how many packets per second (pps) a switch can process, and it varies based on the packet size and the number of switch ports. This rate can be influenced by various factors such as:
--- Packet Size: Switches are tested for packet forwarding using different packet sizes. Smaller packets (64 bytes) typically require more processing power than larger packets (1518 bytes), which can affect the forwarding rate.
--- Port Speed: Higher port speeds result in higher forwarding rates. For example, a switch with 1G ports has a different forwarding rate than one with 10G or 100G ports.
--- Backplane Bandwidth: The internal bandwidth (also known as the backplane) of the switch also affects how fast packets can be forwarded between ports.
Formula to Calculate Packet Forwarding Rate: A switch’s theoretical packet forwarding rate can be calculated using the following formula:
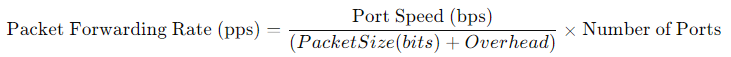
For example, a switch with 24 x 1G ports can theoretically forward 35.7 million packets per second (Mpps) using 64-byte packets, assuming no overhead.
2. Typical Packet Forwarding Rates by Port Speed
Different industrial switches come with varying port speeds and, consequently, different forwarding rates. Below is an estimate of typical packet forwarding rates based on port speeds and the number of ports:
1G (Gigabit Ethernet) Port Forwarding Rate:
--- Each 1G port can forward up to 1.488 Mpps (million packets per second) for 64-byte packets.
--- Example: A switch with 24 x 1G ports will have a theoretical maximum forwarding rate of 35.71 Mpps (24 ports x 1.488 Mpps).
10G (Gigabit Ethernet) Port Forwarding Rate:
--- Each 10G port can forward up to 14.88 Mpps for 64-byte packets.
--- Example: A switch with 8 x 10G ports will have a theoretical maximum forwarding rate of 119 Mpps.
100G Port Forwarding Rate:
--- Each 100G port can forward up to 148.8 Mpps.
--- Example: A switch with 4 x 100G ports will have a maximum forwarding rate of 595 Mpps.
Industrial Switch Example:
An industrial switch with 24 x 1G ports and 4 x 10G uplink ports might have a packet forwarding rate of:
--- 24 x 1.488 Mpps (for 1G ports) = 35.71 Mpps
--- 4 x 14.88 Mpps (for 10G ports) = 59.52 Mpps
--- Total Forwarding Rate: 95.23 Mpps
3. Importance of Packet Forwarding Rate in Industrial Applications
Real-Time Data Processing:
--- In industrial environments such as manufacturing, energy, and transportation, switches are often responsible for managing real-time data from sensors, machines, and controllers. A high packet forwarding rate ensures minimal latency and packet loss, which is critical for real-time communication protocols like Profinet, Modbus, or EtherNet/IP.
Example: In a factory automation setting, an industrial switch may need to handle data from sensors monitoring production line machinery. Any delay in processing packets could cause communication issues, potentially leading to operational disruptions.
High-Density Networks:
--- Industrial switches may need to support a large number of devices, such as IP cameras, PLCs (programmable logic controllers), and HMI (human-machine interfaces). In these high-density networks, a switch with a low forwarding rate could become a bottleneck, causing congestion and affecting network performance.
Mission-Critical Operations:
--- For mission-critical applications in sectors like energy, utilities, and transportation, a high forwarding rate is necessary to ensure that commands and data are transmitted without delay. Any drop in forwarding performance could lead to failures in SCADA systems, remote terminal units (RTUs), or intelligent transportation systems.
4. Switching Capacity vs. Packet Forwarding Rate
--- While packet forwarding rate measures how fast a switch can process and forward packets, switching capacity (or backplane capacity) refers to the total amount of data that can pass through the switch at any given time, typically expressed in Gbps.
Switching Capacity: The overall capacity of the switch’s internal architecture to handle data. For example, a switch with a 48 Gbps backplane can process up to 48 Gbps of data across its ports.
Packet Forwarding Rate: The number of packets the switch can handle per second, typically limited by the port speed and packet size.
Both switching capacity and packet forwarding rate are important to understand when evaluating a switch’s performance. A high switching capacity does not always equate to a high packet forwarding rate, as the switch may still be limited by its ability to process individual packets.
5. Optimizing Packet Forwarding in Industrial Switches
To ensure optimal packet forwarding rates in industrial networks, consider the following:
Port Speed and Count: Ensure that the switch provides enough high-speed ports (such as 10G or 100G) to handle the volume of traffic.
Packet Size Optimization: Industrial switches typically handle a mix of small control packets (e.g., sensor data) and larger data packets (e.g., video streams from IP cameras). Optimizing packet forwarding for both small and large packets can improve network efficiency.
Hardware Acceleration: Some industrial switches feature hardware-based switching engines that can process packets at wire speed, ensuring minimal latency and high forwarding rates.
Buffer Management: Adequate buffering capabilities are important to prevent packet loss during traffic spikes.
6. High-Performance Industrial Switches
In high-performance industrial settings, it’s common to see switches with both high packet forwarding rates and switching capacity. For example:
High-Density Industrial Switches: Some industrial switches come with up to 48 x 1G ports and multiple 10G or 40G uplink ports, designed to handle large volumes of traffic with minimal latency.
Ruggedized Switches: These switches are built for harsh environments and offer wire-speed packet forwarding and high resilience, often supporting redundancy protocols like RSTP, ERPS, and HSR (High-Availability Seamless Redundancy) to ensure uninterrupted packet forwarding.
Conclusion
The packet forwarding rate of industrial switches is a critical measure of their performance, particularly in environments where real-time data exchange, high traffic loads, and mission-critical operations are essential. The forwarding rate depends on the port speed, packet size, and internal architecture of the switch. Typical industrial switches may offer forwarding rates from 1.488 Mpps per 1G port to 148.8 Mpps per 100G port, with scalability depending on the switch model and network demands.
In industrial applications, high packet forwarding rates are essential for maintaining network performance, low latency, and reliability, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, energy, and transportation where uninterrupted communication is critical.