In modern networking, the demand for faster data transmission and long-distance connectivity has led to the rise of Fiber PoE (Power over Ethernet). This hybrid solution leverages the high-speed, long-distance capabilities of fiber optics combined with the convenience of PoE technology, which delivers both power and data over Ethernet cables.
PoE technology allows network devices such as IP cameras, wireless access points, and VoIP phones to receive power and data over the same Ethernet cable. Traditionally, PoE has been popular in environments where running separate power cables would be cumbersome or expensive. PoE technology is governed by several standards, including:
While PoE is excellent for simplifying cabling for shorter distances, its limitation is the 100-meter maximum distance over Ethernet cables. Fiber optic technology, on the other hand, offers solutions for long-distance data transmission, capable of covering several kilometers without signal degradation. Fiber optics use light to transmit data, offering faster speeds and greater resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI) compared to copper cabling.
Fiber PoE setups typically involve a combination of fiber optic cables for long-distance data transmission and Ethernet cables with PoE functionality for delivering power to connected devices. This solution is ideal for network environments where devices need to be located far from the main infrastructure, such as remote IP cameras or wireless access points in large facilities.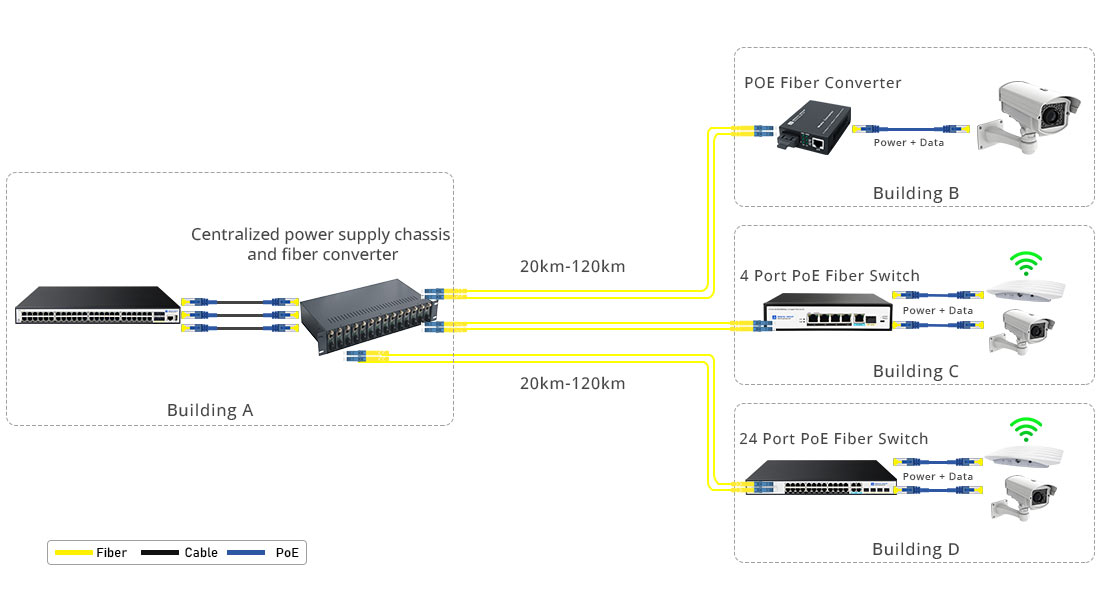
Key Benefits of Fiber PoE:
Extended Reach: Ethernet cables with PoE are limited to a distance of about 100 meters (328 feet). However, by using fiber optic cables for the data portion and PoE for power delivery, networks can achieve extended distances, allowing devices to be placed much farther from the central hub.
Increased Bandwidth: Fiber optics allow for high-speed data transmission, ensuring that the network can handle large amounts of traffic, particularly in applications such as video surveillance or data-intensive industrial automation.
Reduced Infrastructure Costs: While fiber optic installations can be more expensive initially, using a PoE fiber media converter or PoE switch with fiber uplink can reduce the overall costs of running separate power lines to remote devices.
A typical Fiber PoE system includes several components that work together to provide long-distance data transmission and centralized power delivery:
Fiber Optic Cables: These cables handle the data transmission over long distances. Single-mode fiber (SMF) is commonly used for its ability to cover longer distances compared to multi-mode fiber (MMF).
PoE Media Converters or Switches: These devices convert the fiber optic signal into an Ethernet signal and inject power into the Ethernet line to deliver both data and power to PoE-enabled devices. Some PoE switches also come with fiber uplink ports, allowing direct fiber-to-Ethernet connections.
Powered Devices (PDs): End devices such as IP cameras, wireless access points, or VoIP phones receive both power and data via the Ethernet connection.
SFP Modules: Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceivers are often used in fiber PoE setups to handle the conversion of optical signals into electrical signals and vice versa.
Fiber PoE has proven to be a versatile and reliable solution for several industries and applications, particularly where long-distance data transmission and centralized power are critical.
Surveillance Systems: In large-scale security installations such as campuses, airports, or industrial sites, Fiber PoE is ideal for connecting IP cameras that are located far from the network control center. Fiber ensures that high-definition video can be transmitted over long distances, while PoE powers the cameras.
Telecommunications: Telecom providers often use Fiber PoE in the setup of remote base stations or wireless towers, where network connectivity and power delivery must be maintained over long distances. Fiber ensures minimal signal loss, while PoE powers wireless radios or routers.
Smart Cities and IoT Networks: Fiber PoE is critical in smart city applications, where devices like environmental sensors, traffic cameras, and public Wi-Fi access points are distributed across wide areas. Fiber provides the necessary data speeds, and PoE simplifies device installation by removing the need for local power sources.
Manufacturing and Industrial Automation: In factories and industrial sites, Fiber PoE supports remote monitoring systems, where sensors and cameras need to be placed far from control rooms. Fiber handles the large amounts of data, while PoE powers remote sensors and monitoring equipment, reducing the need for additional power infrastructure.
While Fiber PoE offers many advantages, it also presents a few challenges:
Higher Initial Costs: The cost of fiber optic cables, SFP modules, and PoE media converters can be higher than traditional Ethernet-only PoE solutions. However, the extended distance and bandwidth capabilities of fiber often justify these upfront costs for long-term use.
Installation Complexity: Fiber optic cables require specialized installation and handling due to their fragility and the need for precise splicing. This often requires trained personnel, adding to the installation costs and time.
Compatibility: Not all PoE devices are compatible with fiber PoE setups. Network planners need to ensure that the PoE devices (like cameras or access points) can be connected to the fiber network via media converters or PoE switches with fiber ports.
It can be seen that for network environments where long-distance data transmission, high bandwidth, and centralized power supply are critical, fiber PoE is a powerful and scalable solution. It combines the advantages of fiber and the convenience of PoE, providing a flexible and reliable option for industries such as telecommunications and security surveillance. Although the upfront cost is high and the installation is complex, the long-term advantages in network performance, stability, and scalability make fiber PoE a key component of modern network infrastructure.
By leveraging fiber PoE, companies can build more efficient, cost-effective, and higher-performance networks to meet the growing needs of today's connected world.