Power over Ethernet (PoE) and Power over Ethernet Plus (PoE+) are technologies that enable the transmission of both data and electrical power through a single Ethernet cable. These technologies have become essential in modern networking, particularly for powering devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points. However, there are key differences between PoE and PoE+ switches that impact their applications, performance, and compatibility.
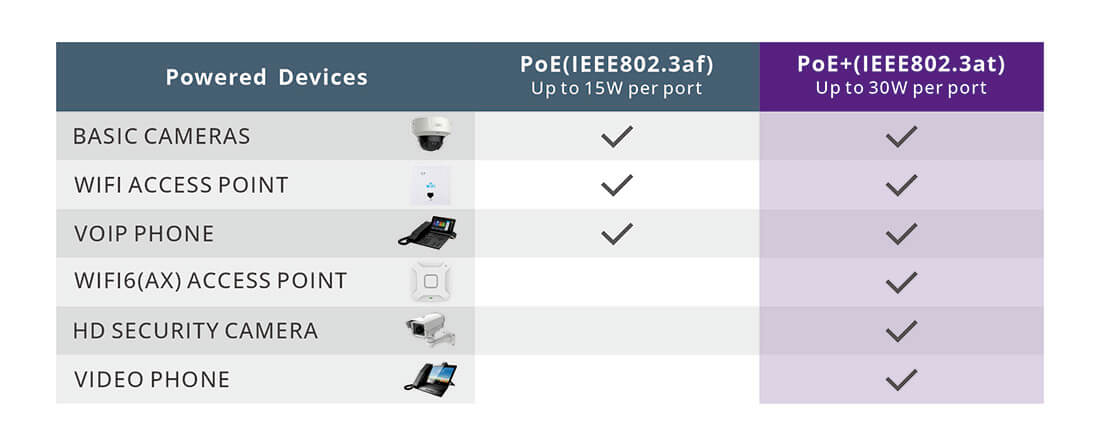
The most significant difference between PoE and PoE+ switches lies in their power delivery capabilities. PoE, defined under the IEEE 802.3af standard, can deliver up to 15.4 watts of power per port. This is sufficient for many low-power devices, such as standard IP cameras and VoIP phones. However, as the demand for more power-hungry devices has grown, the need for higher power delivery led to the development of PoE+.
PoE+, defined under the IEEE 802.3at standard, can deliver up to 30 watts of power per port, nearly double the capacity of PoE. This increased power is necessary for devices like pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) cameras, which require more energy for their motors, or for wireless access points that need to cover larger areas or support more users. The ability to deliver more power makes PoE+ a more versatile choice for environments with diverse device requirements.
Both PoE and PoE+ switches use standard Ethernet cables, but there are differences in the type of cable required to maximize performance. PoE switches typically work well with Cat5e cables, which are sufficient to carry the 15.4 watts of power without significant loss. However, PoE+ switches, due to their higher power output, perform better with Cat6 cables or higher. These cables have lower resistance, which helps in minimizing power loss over longer distances, making them a better choice for PoE+ applications.
Compatibility is another crucial factor to consider when choosing between PoE and PoE+ switches. PoE+ switches are backward compatible with PoE devices, meaning you can connect a PoE device to a PoE+ switch, and it will function properly, receiving the appropriate amount of power. However, the reverse is not true: PoE switches cannot provide sufficient power for PoE+ devices, which could result in devices not functioning correctly or at all.
Cost is always a significant factor in any technology decision. Generally, PoE+ switches are more expensive than PoE switches due to their enhanced capabilities. The additional cost comes from the increased power output and the need for better thermal management and power regulation within the switch. However, the higher cost of PoE+ switches may be justified in environments where future-proofing is important, or where high-power devices are in use.
PoE switches are ideal for environments with standard networking devices that have low to moderate power requirements, such as small offices or homes with basic IP phones, cameras, and access points. On the other hand, PoE+ switches are better suited for more demanding environments, such as large offices, campuses, or industrial settings where devices like PTZ cameras, advanced access points, and other high-power devices are deployed.
The choice between PoE and PoE+ switches depends on your specific needs. If your network consists of devices with lower power requirements, a PoE switch may suffice. if you’re planning to power devices with higher power requirements or anticipate future expansion of your network, choosing a higher POE standard (such as POE+ or POE++) might be beneficial. However, always make sure to verify compatibility, assess the capabilities of your existing infrastructure, and consider your specific needs before making a decision.make an informed choice that ensures your network's efficiency and longevity.